Matplotlib
Matplotlib 是用于创建图表的 Python 库。 Matplotlib 可用于 Python 脚本,Python 和 IPython shell,jupyter 笔记本,Web 应用服务器以及四个图形用户界面工具包。
Matplotlib 安装
Matplotlib 是需要安装的外部 Python 库。
我们可以使用pip工具安装该库。
Matplotlib 散点图
散点图是一种图形或数学图,使用笛卡尔坐标显示一组数据的两个变量的值。
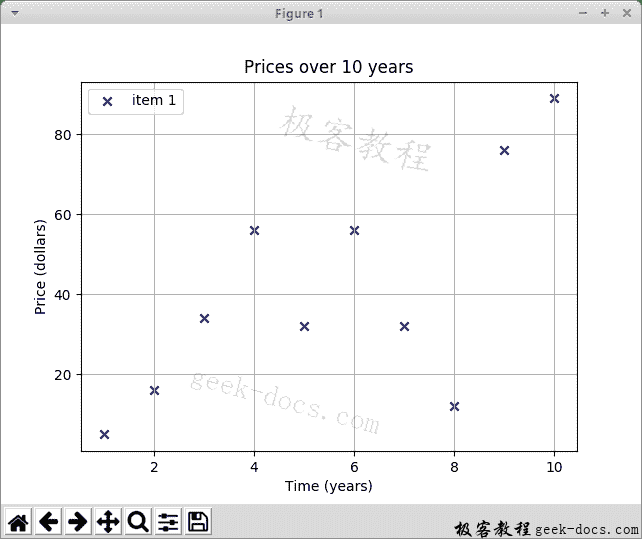
scatter.py
该示例绘制了一个散点图。 该图表显示了十年内某些商品的价格。
我们从matplotlib模块导入pyplot。 它是创建图表的命令样式函数的集合。 它的操作与 MATLAB 类似。
我们有 x 和 y 轴的数据。
通过title()功能,我们可以为图表设置标题。
scatter()功能绘制散点图。 它接受 x 和 y 轴,标记的颜色,标记的形状和标签的数据。
我们为轴设置标签。
我们用grid()功能显示网格。 网格由许多垂直和水平线组成。
legend()功能在轴上放置图例。
show()功能显示图表。
两个数据集
在下一个示例中,我们将另一个数据集添加到图表。
scatter2.py
该图表显示两个数据集。 我们通过标记的颜色来区分它们。
我们有两个数据集。
我们为每个集合调用scatter()函数。
Matplotlib 折线图
折线图是一种显示图表的图表,该信息显示为一系列数据点,这些数据点通过直线段相连,称为标记。
linechart.py
该示例显示正弦波折线图。
在示例中,我们还需要numpy模块。
arange()函数返回给定间隔内的均匀间隔的值列表。
我们获得数据的sin()值。
我们使用plot()功能绘制折线图。
Matplotlib 条形图
条形图显示带有矩形条的分组数据,其长度与它们代表的值成比例。 条形图可以垂直或水平绘制。
barchart.py
该示例绘制了条形图。 它显示了 2012 年伦敦每个国家/地区的奥运金牌数量。
可以使用预定义的样式。
subplots()函数返回图形和轴对象。
使用bar()功能生成条形图。
我们为 x 轴设置国家/地区名称。
Matplotlib 饼图
饼图是圆形图,将其分成多个切片以说明数值比例。
piechart.py
该示例创建一个饼图。
我们有标签和相应的数量。
我们为饼图的切片定义颜色。
饼图是通过pie()功能生成的。 autopct负责在图表的楔形图中显示百分比。
我们设置了相等的长宽比,以便将饼图绘制为圆形。

 seo优化_前端开发_渗透技术
seo优化_前端开发_渗透技术


